the gold standard of minimally invasive treatment for an enlarged prostate
What is Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)?
BPH, benign prostatic hyperplasia, is a condition in which the prostate is enlarged. With BPH, there is an overgrowth of prostate tissue which pushes against the urethra and the bladder, blocking the flow of urine.
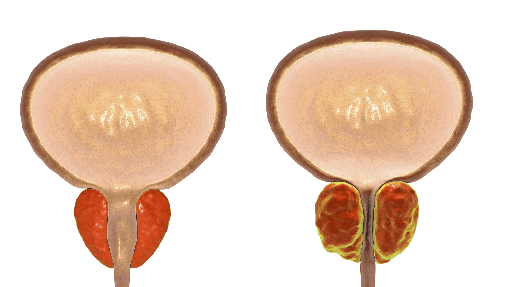
Normal Prostate (left) vs Enlarged Prostate (right)

What is Endoscopic Enucleation of the Prostate (EEP)?
Endoscopic enucleation of prostate is a minimally invasive treatment for an enlarged prostate. The procedure most commonly involves a laser fiber (LEEP) to remove tissue that is blocking urine flow through the prostate. LEEP outcomes are similar to open prostate surgery but requires no incisions. The procedure goal is to remove the entire portion of the prostate that can block urine flow with no incision, like peeling an orange slice from the rind.
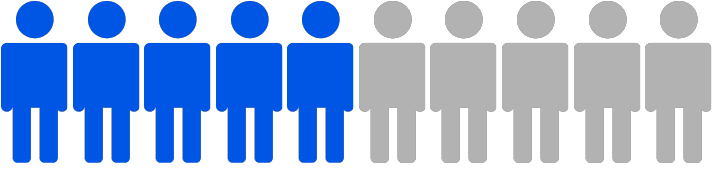
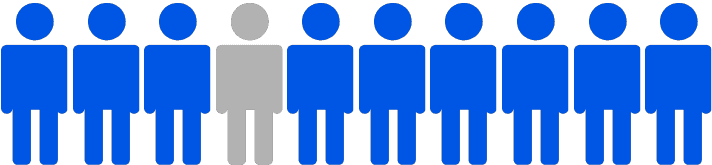
BPH is common in men over the age of 50.
%
of men between the ages of 51 and 60 will have signs of this condition
%
of men over the age of 80 will have signs of this condition
Signs, Symptoms, & Treatments
Your doctor is best positioned to help you find the root cause of your urinary problems. Learning more about the various signs & symptoms of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) and how it can be treated will help you guide the conversation with your doctor.
How Does EEP Work?
Prostate laser surgery can be used to relieve moderate to severe urinary symptoms that may be caused by BPH. Do you want to learn more about what you can expect?
Are You Curious If You May
Be Struggling With BPH?
BPH News
Hear About the Latest Medical Advancements
Fewer Side Effects and Faster Recovery with HoLEP Treatment
January 03, 2017 by University Hospitals - Urology Institute A new treatment called HoLEP (holmium laser enucleation of the prostate) removes all extra tissue from the prostate without an invasive incision. It’s effective on all sizes of prostates, has no risk of...
HoLEP vs. TURP
Sascha A. Ahyaia, Karin Lehrich, Rainer M.Kuntz European Urology. Volume 52, Issue 5, November 2007, Pages 1456-1464 200 patients were randomly assigned either HoLEP or TURP as their treatment and followed over three years. The results? All indicators of prostate...
Outpatient Surgery vs. Inpatient Stay for HoLEP on Larger Prostates
Mark A. Assmus, Tim Large, Matthew S. Lee, Deepak K. Agarwal, Marcelino E. Rivera, and Amy E. Krambeck Journal of Endourology. Published Online: 17 Mar 2021 Advances in laser technology and surgical technique are showing early evidence to support outpatient surgery....
References
1. AskMayoExpert. Holmium laser enucleation of the prostate. Rochester, Minn.: Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research; 2018.
2. Shigemura K, et al. Current status of holmium laser enucleation of the prostate. International Journal of Urology. 2018;25:206.
3. Wein AJ, et al., eds. Minimally invasive and endoscopic management of benign prostatic hyperplasia. In: Campbell-Walsh Urology. 11th ed. Philadelphia, Pa.: Elsevier; 2016. https://www.clinicalkey.com Accessed May 23, 2019.
4. McAdams S, et al. Morcellation efficiency in holmium laser enucleation of the prostate: Oscillating morcellator outperforms reciprocating morcellator with no apparent learning curve. Urology. 2017;106:173.
5. Ibrahim A, et al. Eighteen years of holmium laser enucleation of the prostate: A single center experience. Journal of Urology. In press. Accessed May 25, 2019.
6. Kuebker JM, et al. Holmium laser enucleation of the prostate: Patient selection and outcomes. Current Urology Reports. 2017;18:96.
7. Tominaga Y, et al. Favorable long term oncological and urinary outcomes of incidental prostate cancer following holmium laser enucleation of the prostate. Molecular and Clinical Oncology. 2019;10:605.
8. Warner KJ. Allscripts EPSi. Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn. May 6, 2019.
9. Stern KL. A new laser platform for holmium laser enucleation of the prostate: Does the Lumenis Pulse 120H laser platform improve enucleation efficiency? Urology. 2017;102:198.


